Are you experiencing symptoms and wondering if you have a urinary tract infection (UTI)? This article will cover the best ways to test for UTI, detail common symptoms, explain how to use home test kits, and when to seek medical advice.
Key Takeaways
- UTIs are more prevalent in women due to anatomical factors, and certain populations, including diabetics and post-menopausal women, are at increased risk.
- Recognizing UTI symptoms early, such as frequent urination and a burning sensation, is essential to prevent complications like kidney infections.
- Effective UTI treatment primarily involves antibiotics, but prevention strategies, including hydration and possible low-dose antibiotics, are critical for those with recurrent infections.
Understanding Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
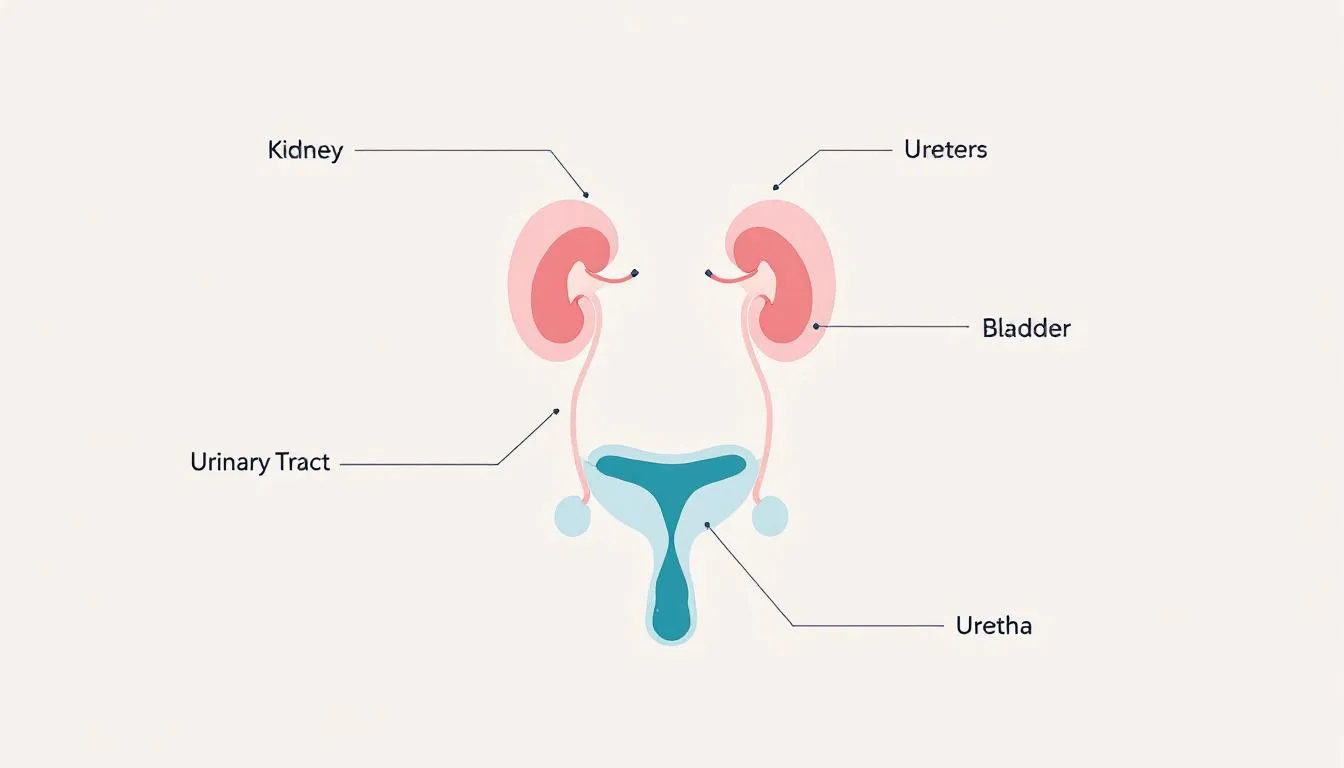
A urinary tract infection (UTI) occurs when bacteria infiltrates the urinary tract, which encompasses the kidneys, bladder, and urethra. These infections can affect multiple parts of the urinary system, resulting in conditions like bladder infections (cystitis) or more severe kidney infections (pyelonephritis). Knowing what UTIs are and their effects on the body is crucial for effective management and prevention.
Women are particularly susceptible to UTIs due to their shorter urethras, which provide bacteria such as Escherichia coli (E. coli) easier access to the bladder. Most women experience factors like structural abnormalities in the urinary tract, such as diverticula or blockages, and the use of devices like catheters, which can further increase the likelihood of infection. For men, an enlarged prostate can significantly heighten the risk of developing UTIs.
Certain groups are at a heightened risk of UTIs, which includes an increased risk for diabetics, due to their compromised ability to fight off infections. Users of some birth control methods, such as diaphragms and spermicidal condoms, can increase UTI susceptibility. Post-menopausal women, because hormonal changes affect the vaginal lining.
Sexual activity can elevate the frequency of UTIs, especially in women who are sexually active, as it can usher bacteria into the urinary tract. Some women are genetically predisposed to UTIs due to urinary tracts that facilitate bacterial adhesion. Recognizing these risk factors can help in taking proactive steps to prevent UTIs.
Recognizing UTI Symptoms
The symptoms of a urinary tract infection are often unmistakable. They include:
- Frequent urinating
- A persistent urge to urinate
- A burning sensation during urination
- To pass urine in small amounts frequently
These symptoms can be incredibly discomfort and disruptive to daily life.
In addition to these common symptoms, UTIs can cause pain in the abdomen, flank, or lower back, indicating that the infection might be spreading. Sometimes, the urine may appear cloudy or have an unusual odor, both of which are indicative of an infection. It’s crucial to recognize these signs early to seek appropriate treatment promptly.
When a lower UTI is left untreated, it can progress to a kidney infection. Symptoms of kidney infections include fever, chills, and significant flank pain. These symptoms are more severe and indicate that the infection has moved deeper into the urinary system, necessitating urgent medical attention.
Older adults might not exhibit typical symptoms; instead, they could experience confusion or other symptoms.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Experiencing uncomplicated uti symptoms should prompt you to contact your healthcare provider swiftly for timely treatment. Early intervention can prevent the infection from escalating into more severe complications. Even if the symptoms seem mild, seeking medical advice ensures you are on the right track.
Severe symptoms such as persistent pain, fever, or the presence of blood in your urine necessitate immediate medical attention. Blood in urine is a significant red blood cells red flag that should not be ignored. Untreated kidney infections can lead to serious complications, making it crucial to address these symptoms without delay.
Home tests for UTIs offer a quick preliminary assessment but are not foolproof and may miss some cases. Consulting a healthcare provider is particularly important if you have a history of recurrent UTIs. If symptoms worsen or include vomiting and fever that do not improve with treatment, seek professional medical advice immediately.
Diagnostic Methods for UTIs
Diagnosing a urinary tract infection often starts with analyzing a urine sample to detect bacteria and white blood cells indicating an infection. A dipstick test can also be performed on the urine sample to detect leukocyte esterase and nitrites, both of which suggest a bacterial UTI.
Urine cultures are another crucial diagnostic tool, as they help confirm the presence of a UTI and identify the specific bacteria causing the infection. Accurate sample collection is vital to avoid contamination, which could lead to incorrect culture results. Proper collection techniques significantly improve diagnosis reliability.
These diagnostic methods help determine the appropriate treatment plan. In some cases, further tests may be needed to rule out other conditions or to tailor the treatment to the specific type of bacteria identified in the urine culture.
Additional Tests for Complicated UTIs
When dealing with complicated UTIs, additional diagnostic methods are often required. Imaging tests, such as a CT scan, can provide detailed images of the urinary tract, helping to identify underlying issues like obstructions or abscesses. These tests are particularly useful when a kidney infection is suspected or when symptoms are more severe.
Specialist referrals to urologists are sometimes necessary for managing recurrent or complicated UTIs that are difficult to treat. A urologist can offer more specialized care and recommend further diagnostic tests or treatments tailored to the individual’s condition.
Home Testing Kits for UTIs
Home testing kits for UTIs have become increasingly popular due to their convenience and ease of use. Kits like the TouchBio UTI Test offer:
- An accuracy of over 98%
- Results delivered in just two minutes
- Easy self-testing without the need for special training
- Quick interpretation of results by individuals
These home testing kits typically consist of dipstick tests that detect the presence of leukocyte esterase and nitrites in urine, indicating potential infections. While these kits are highly accurate, they are not a substitute for professional medical advice and should be used as a preliminary assessment tool.
The benefits of home testing kits include their speed and convenience, making them particularly useful for individuals who experience recurrent UTIs. However, they have limitations and cannot replace a comprehensive medical evaluation, especially for complicated cases.
Treatment Options for UTIs

The primary treatment for bacterial UTIs is antibiotics. Commonly prescribed antibiotics include nitrofurantoin, sulfa drugs, and amoxicillin. It’s essential to complete the full course of antibiotics to ensure the infection is entirely eradicated and to prevent it from returning. Healthcare providers often prescribe antibiotics for these infections.
In cases where the UTI is resistant to standard antibiotics, treatment options include:
- Intravenous treatment, including iv antibiotics, may be necessary.
- If symptoms persist after the initial treatment, a different antibiotic or a longer course may be required.
- Using the appropriate antibiotic based on the specific bacteria identified in the urine culture is crucial for effective treatment.
Treatment options also include managing symptoms and preventing recurrence. For recurrent UTIs, low-dose antibiotics may be prescribed for a short duration to prevent frequent infections. It’s important to follow the prescribed treatment plan and consult with your healthcare provider if you have any concerns about treating your condition. If left unaddressed, infections can lead to complications that should be treated promptly.
Preventing Recurrent UTIs

Preventing recurrent UTIs is vital as they can lead to serious complications if left untreated. One of the simplest and most effective preventive measures is to drink plenty of water, which helps flush out bacteria from the urinary tract. Staying hydrated is a key strategy to prevent UTIs.
Cranberry products extract supplements have also been shown to decrease the chances of developing a UTI. Individuals with recurrent UTIs may be advised to take preventive antibiotics. Short-term, low-dose antibiotics can help reduce infection frequency.
Other preventive measures include using vaginal estrogen cream for post-menopausal women to help maintain a healthy vaginal lining. Methenamine hippurate is another non-antibiotic alternative that can be explored for preventing UTIs. Taking these steps can significantly reduce the risk of recurrent infections.
Potential Complications from Untreated UTIs
Untreated urinary tract infections can lead to serious complications such as kidney infections or sepsis. Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when the body’s response to infection causes widespread inflammation. About 3% of UTIs can progress to kidney infections, known as pyelonephritis.
Certain groups, including individuals over 65, those with diabetes, and people with weakened immune systems, are at a higher risk for severe complications from untreated UTIs. Prompt recognition and treatment of UTIs are crucial to avoid serious health issues.
Summary
Understanding UTIs, recognizing their symptoms, seeking timely medical advice, and following preventive measures are crucial steps in managing this common condition. By being proactive and informed, you can significantly reduce the risk of complications and ensure better health outcomes. Take control of your health, consult with healthcare providers when needed, and stay vigilant about preventive measures to keep UTIs at bay.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of a UTI?
The common symptoms of a UTI are frequent urination, a burning sensation during urination, and urine that appears cloudy or has a foul odor. It is important to consult a healthcare professional if you experience these symptoms.
When should I seek medical advice for a UTI?
You should seek medical advice for a UTI if you experience severe symptoms such as persistent pain, fever, or blood in your urine, as these could indicate a more serious condition. Timely consultation can ensure proper treatment and prevent complications.
How are UTIs diagnosed?
UTIs are diagnosed primarily through the analysis of urine samples, which may include dipstick tests and urine cultures. This thorough examination aids in identifying the presence of bacteria and other indicators of infection.
What are the treatment options for UTIs?
The primary treatment for urinary tract infections (UTIs) is antibiotics, and it is crucial to complete the entire course to effectively eradicate the infection.
How can I prevent recurrent UTIs?
To prevent recurrent UTIs, it is essential to drink plenty of water, consider cranberry extract supplements, and discuss preventive antibiotics with your healthcare provider if necessary. Implementing these strategies can significantly reduce the likelihood of future infections.